How Transistors Work – A Simple Explanation
The transistor is like an electronic switch. It can turn a current on and off. A simple way you can think of it is to look at the transistor as a relay without any moving parts. A transistor is similar to a relay in the sense that you can use it to turn something ON and OFF.
There are different types of transistors. A very common one is the “bipolar junction transistor” or “BJT”. And it usually looks like this:
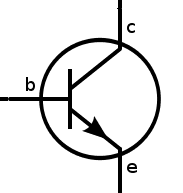
It has three pins: Base (b), collector (c) and emitter (e). And it comes in two versions: NPN and PNP. The schematic symbol for the NPN looks like this:
How transistors work is probably the hardest concept for you to understand as a beginner. At least it was for me.
The problem is that almost everyone is trying to teach that a transistor is “…a semiconductor device”. And instead of just telling you what it does, they explain that “…it consists of n-doped and p-doped materials”.
I don’t know about you, but that statement didn’t help me much!
So let me tell you, in a simple way, how transistors work. I even made a video for you, just to make it clearer.
The transistor is like an electronic switch. It can turn a current on and off. A simple way you can think of it is to look at the transistor as a relay without any moving parts. A transistor is similar to a relay in the sense that you can use it to turn something ON and OFF.
There are different types of transistors. A very common one is the “bipolar junction transistor” or “BJT”. And it usually looks like this:

It has three pins: Base (b), collector (c) and emitter (e). And it comes in two versions: NPN and PNP. The schematic symbol for the NPN looks like this:

How transistors work
The transistor works because of something called a semiconducting material. A current flowing from the base to the emitter “opens” the flow of current from the collector to the emitter.
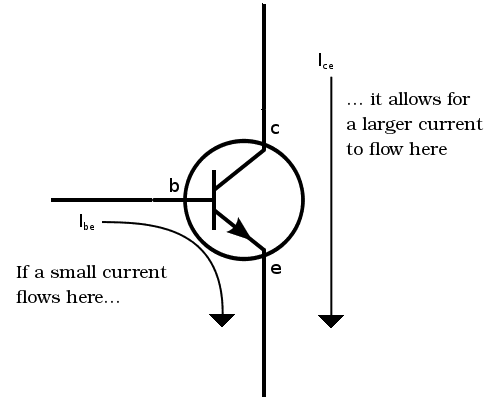
In a standard NPN transistor, you need to apply a voltage of about 0.7V between the base and the emitter to get the current flowing from base to emitter. When you apply 0.7V from base to emitter you will turn the transistor ON and allow a current to flow from collector to emitter.
Let’s look at an example:
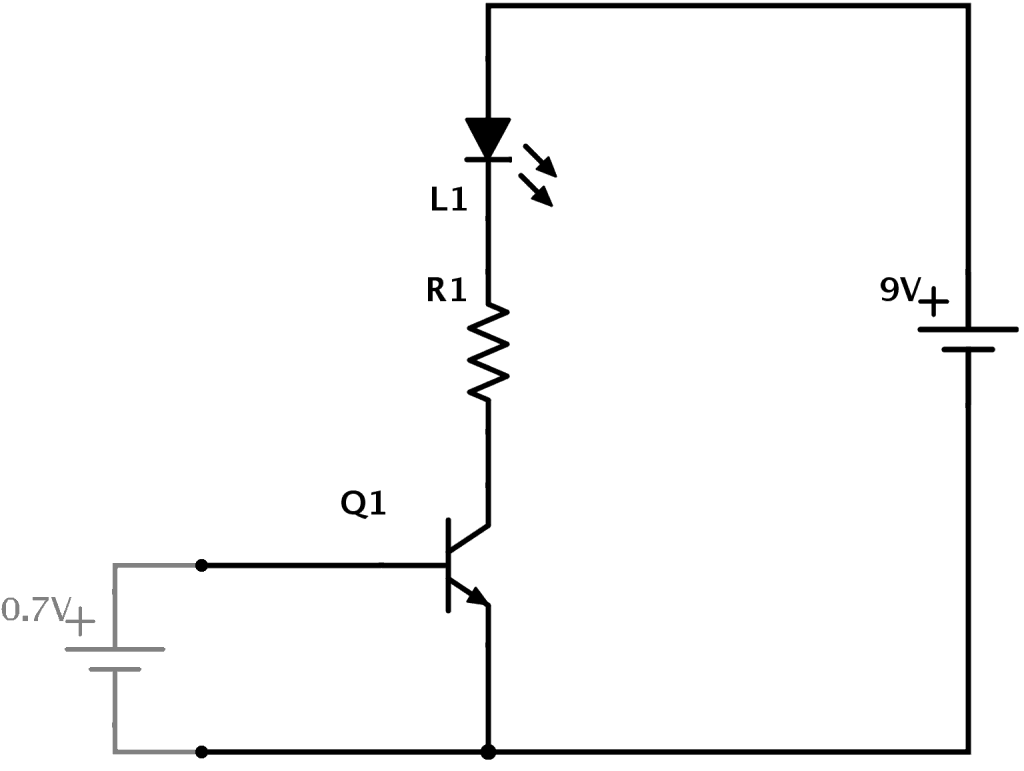
In the example above you can see how transistors work. A 9V battery connects to an LED and a resistor. But it connects through the transistor. This means that no current will flow in that part of the circuit until the transistor turns ON.
To turn the transistor ON you need to apply 0.7V from base to emitter of the transistor. Imagine you have a small 0.7V battery. (In a practical circuit you would use resistors to get the correct voltage from whatever voltage source you have)
When you apply the 0.7V battery from base to emitter, the transistor turns ON. This allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter. And thereby turning the LED ON!


Post a Comment